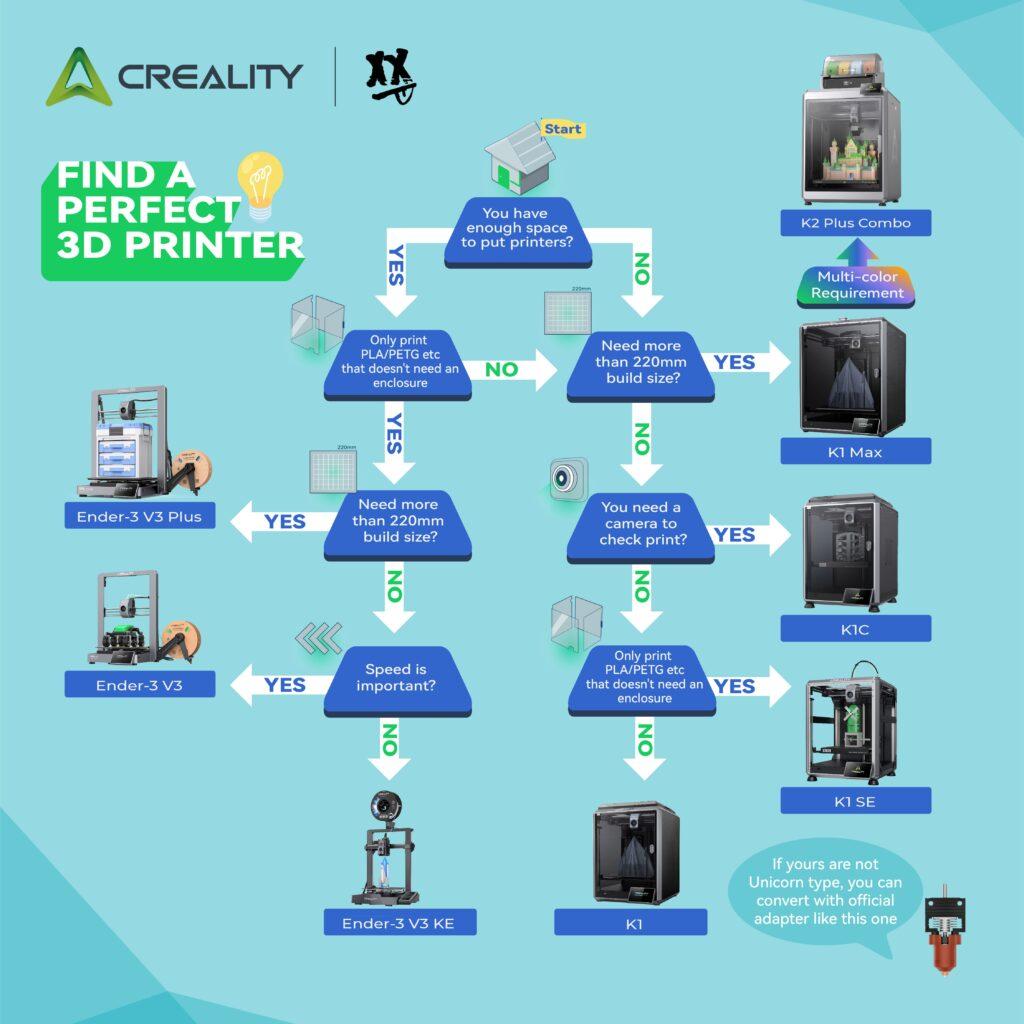
Ever wanted to make your own tools, invent cool gadgets, or bring your imagination to life? 3D printing is making that possible! Learn how hobbyists, teachers, and everyday folks use this fantastic technology to change the world, one layer at a time.
The Rise of the Maker Revolution
Imagine, if you will, a world where the boundaries of creation are not limited by the constraints of traditional manufacturing. A world where the power to bring forth tangible objects from the realm of imagination rests not in the hands of distant factories, but quite literally at your fingertips, within the cozy confines of your own home. This isn’t a scene plucked from a futuristic fantasy; it’s the burgeoning reality of today, made possible by the transformative technology of 3D printing.
It wasn’t so long ago that 3D printing seemed like a concept confined to the sterile environments of advanced laboratories and the humming, colossal spaces of industrial complexes. Back then, it was an esoteric and expensive process, a tool wielded by white-coated scientists and meticulous engineers to craft prototypes and highly specialized components. The machines themselves were behemoths of metal and wire, intimidating in their complexity and prohibitive in their cost.
But, as technological progress often does, things have changed dramatically. The once-formidable barriers of cost and complexity have crumbled, giving way to a new era of accessibility. 3D printers, sleek and increasingly user-friendly, are now finding their place in homes, schools, and workshops, much like personal computers did a few decades prior. This democratization of manufacturing, this shift from centralized production to distributed creation, has ignited a spark – a “maker revolution” – that is rapidly reshaping our world.
At the heart of this revolution are the hobbyists, those passionate individuals who have always loved tinkering, inventing, and building. These are the people who, in a previous era, might have been relegated to tinkering in garages and basements, their ingenuity limited by the tools and resources at their disposal. But now, armed with the power of 3D printing, they are unleashing their creativity in ways that were once thought impossible. It’s not just about crafting cool toys or funky art projects, though there’s certainly plenty of that happening. It’s about a fundamental shift in how we learn, how we approach problem-solving, and how we interact with the very fabric of our material world.
So, what is it about 3D printing that has captured the imagination of so many? What is the “big deal” that has everyone so excited? In the narrative that follows, we will embark on an exploration of this captivating technology, delving into the myriad ways it is empowering hobbyists, students, and everyday people to transform themselves into creators, inventors, and problem-solvers. We will examine how 3D printing is revolutionizing DIY projects, making STEM education more dynamic and engaging, and providing innovative solutions to the challenges of daily life. Prepare to have your perceptions challenged and your imagination ignited, for the world of 3D printing is a world where the only limit is the reach of your dreams.
3D Printing in DIY Projects: Unleashing Your Inner Inventor
We have all experienced that moment of frustration, that spark of ingenuity stifled by the limitations of the physical world. “If only I could make this thing myself,” we muse, whether it’s a specialized tool for a particular project or a brilliant idea for a new gadget that exists only in the realm of our imagination. In the past, such aspirations often remained just that – aspirations. The path from concept to creation was a long and arduous one, fraught with obstacles such as expensive tooling, complex manufacturing processes, and the sheer difficulty of obtaining custom-made parts. But 3D printing has emerged as a veritable superpower for DIY enthusiasts, a technological alchemy that transmutes ideas into tangible reality. It is akin to having a magic workshop, a place where the raw materials of imagination are molded and shaped into functional objects with astonishing ease.
A. Prototyping and Iteration: From Idea to Awesome
The process of invention, as depicted in countless films and historical accounts, is rarely a linear progression from inspiration to flawless product. Rather, it is a cyclical journey of trial and error, a dance of creation and refinement. Inventors, throughout history, have been characterized by their tireless pursuit of perfection, their willingness to experiment, to fail, and to rise again, armed with new knowledge and insights. This iterative process, known as “prototyping and iteration,” is fundamental to bringing any new idea to fruition. And in the past, it was often a major bottleneck, a time-consuming and costly endeavor.
- 1. Rapid Design and Testing: In the days before 3D printing, the creation of a prototype was a complex and often protracted affair. If an inventor conceived of a new design, whether it was a part for a machine, a new type of tool, or even a simple household object, the process of bringing that design into the physical world typically involved the creation of molds, the casting of parts, and a significant investment of both time and resources. Weeks, or even months, could elapse between the initial conceptualization of an idea and the moment when a tangible prototype could be held in one’s hand. This glacial pace severely hampered the inventive process, limiting the number of ideas that could be explored and the speed at which designs could be improved.
- 2. Efficient Project Refinement: But 3D printing has ushered in a new era of rapid prototyping, shattering the constraints of traditional manufacturing. With a 3D printer, a designer can translate a digital design into a physical object in a matter of hours. This ability to swiftly produce tangible prototypes has profound implications for the process of invention. It means that ideas can be tested and evaluated in the real world with unprecedented speed, allowing designers to identify flaws, assess functionality, and gather feedback much earlier in the development cycle. More importantly, it transforms the process of refinement. If the initial prototype is not perfect, as is so often the case, the designer can simply tweak the digital model and print a new version. This iterative cycle of design, printing, testing, and refinement can be repeated multiple times in a single day, allowing for a degree of optimization that was simply unattainable in the past. The result is a process of design that is not only faster but also more dynamic, more responsive, and ultimately, more likely to yield successful outcomes.
- 3. Examples: Custom Enclosures, Mechanical Parts: The applications of 3D printing in DIY projects are as diverse as the imaginations of the DIYers themselves. Consider the example of a hobbyist building a smart home controller, a device that integrates various electronic systems and allows them to be controlled from a central interface. In the past, this project would have been complicated by the challenge of finding a suitable enclosure for the delicate electronic components. Generic plastic boxes might have been used, but these often lacked the precise fit and aesthetic appeal that the project demanded. With 3D printing, however, the hobbyist can design and print a custom enclosure that not only perfectly accommodates the components but also reflects the overall design aesthetic of the project. The result is a device that is both functional and visually appealing, a testament to the power of 3D printing to elevate DIY projects to a new level of professionalism. Or imagine a DIYer constructing a robot, a complex assembly of motors, sensors, and structural elements. 3D printing empowers the creator to produce specialized mechanical parts, such as gears, brackets, and joints, with a level of precision that would have been difficult and expensive to achieve using traditional machining techniques. This ability to create custom mechanical components opens up a world of possibilities for robotics enthusiasts, allowing them to design and build increasingly sophisticated and capable machines.
B. Customization and Personalization: Make It Yours
Beyond its ability to accelerate the prototyping process, 3D printing offers DIYers a unique opportunity to infuse their creations with a personal touch, to tailor them to their specific needs and preferences in a way that mass-produced products simply cannot match. In a world where so many of the objects we use in our daily lives are churned out in factories, identical in form and function, 3D printing empowers individuals to express their individuality and to create things that are truly one-of-a-kind.
- 1. Tailoring Designs to Specific Needs: How often have we purchased a tool or a gadget that was “almost perfect,” but not quite? Perhaps the handle was slightly too small for our hand, or the grip was not optimized for our particular style of use. With 3D printing, the era of “almost perfect” is drawing to a close. DIYers can now design tools that are precisely tailored to their ergonomic requirements, ensuring maximum comfort and efficiency.
- 2. Creating Unique Tools and Décor: But the applications of 3D printing extend far beyond the realm of tools. This technology can also be used to create unique décor items that reflect the individual’s personal style and taste. A hobbyist can design a set of vases with intricate geometric patterns or a series of coasters adorned with custom-designed motifs. Even jewelry, that most personal of adornments, can be brought into being through the artistry of 3D printing, allowing individuals to express themselves through wearable art that is as unique as they are.
- 3. Examples: Ergonomic Handles, Organizers, Personalized Items: Consider the humble tool, an object that is often taken for granted but that plays a crucial role in countless DIY projects. With 3D printing, a DIYer can design ergonomic handles for their favorite tools, optimizing them for comfort and reducing the risk of strain or injury during prolonged use. Or imagine a workshop or craft room, a space that can quickly become cluttered and disorganized. 3D printing offers a solution in the form of custom-designed organizers, each one meticulously crafted to accommodate specific tools and materials, ensuring that everything is kept neat, tidy, and readily accessible. And then there are the possibilities for personalized gifts. A 3D-printed phone stand bearing the recipient’s name, a set of custom-designed keychains that reflect their hobbies or interests – these are just a few examples of the countless ways in which 3D printing can be used to create meaningful and memorable presents that speak to the unique bond between giver and receiver.
C. Repair and Replacement: Fix It Yourself!
In our consumer-driven society, the prevailing ethos often seems to be one of disposability. When something breaks, the reflex is often to simply discard it and purchase a new one, regardless of whether the broken component is a small, easily replaceable part. This throwaway culture not only places a significant burden on our landfills but also fosters a sense of helplessness, a feeling that we are at the mercy of manufacturers and their design decisions. But 3D printing is empowering individuals to reclaim their agency, to challenge this culture of disposability, and to embrace a more sustainable and self-reliant approach to repairs.
- 1. Printing Replacements for Broken Parts: Instead of consigning a perfectly functional appliance to the scrap heap because of a broken plastic part, individuals can now turn to 3D printing to create a replacement. This simple act of repair, once a daunting and often futile endeavor, is now within the reach of anyone with access to a 3D printer and the requisite design skills.
- 2. Extending Product Lifespans: The implications of this ability to print replacement parts are profound. By extending the lifespan of our products, we not only save money but also reduce our environmental footprint. Less waste ends up in landfills, and the demand for new products, with all the resource extraction and energy consumption that they entail, is lessened. In a world grappling with the challenges of sustainability, 3D printing offers a tangible pathway towards a more circular economy, where resources are valued and waste is minimized.
- 3. Examples: Appliance Parts, Fittings, Components: The range of items that can be repaired with 3D printed parts is vast and continues to expand. A broken handle on a refrigerator drawer, a missing knob on a stove, a set of stripped gears in a child’s toy – these are just a few examples of the countless everyday items that can be restored to functionality with a 3D-printed replacement. As 3D printing technology becomes more sophisticated and accessible, it is empowering people to become more self-sufficient, more resourceful, and less reliant on a system that often seems designed to encourage consumption rather than repair.
D. Artistic Expression: 3D Printing Meets Art
While 3D printing is often associated with practical applications, its impact extends far beyond the realm of the functional. It is also a powerful medium for artistic expression, a technology that is enabling artists to push the boundaries of creativity and to explore new forms of aesthetic expression.
- 1. Creating Intricate Sculptures: Artists are harnessing the precision and geometric freedom of 3D printing to create sculptures of breathtaking complexity. Intricate forms and structures, once deemed impossible using traditional sculpting methods, can now be realized with astonishing fidelity.
- 2. Combining 3D Printing with Traditional Arts: But 3D printing is not merely replacing traditional art forms; it is also being integrated with them, giving rise to exciting new hybrid forms of artistic expression. Jewelers are incorporating 3D-printed elements into their designs, combining the precision of digital fabrication with the timeless beauty of handcrafted artistry.
- 3. Examples: Jewelry, Art Pieces, Cosplay Props: The influence of 3D printing can be seen in art galleries, where avant-garde sculptures challenge our perceptions of form and space, and on the convention floor, where cosplayers don elaborate, 3D-printed props that blur the line between fantasy and reality. 3D printing is a technology that is not only inspiring creativity but also democratizing it, making the tools of artistic production more accessible to a wider range of creators.

3D Printing in STEM Education: The Future is Now
The winds of change are blowing through the hallowed halls of education, and at the forefront of this transformation is the disruptive yet promising technology of 3D printing. For generations, the teaching of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) has often relied heavily on abstract concepts and theoretical frameworks, presented through the medium of textbooks and lectures. But 3D printing is injecting a new dynamism into STEM education, a hands-on, minds-on approach that is making learning more engaging, more relevant, and more effective.
A. Hands-on Learning: Learning by Doing
The traditional classroom, with its rows of desks and its emphasis on passive listening, is gradually giving way to a more interactive and experiential model of learning. And 3D printing is playing a key role in this shift, transforming abstract concepts into tangible realities.
- 1. Tangible Experiences with Abstract Concepts: Imagine a student struggling to grasp the intricacies of molecular structure, the spatial relationships between atoms, and the dynamic forces that govern their interactions. In the past, this student would have been confined to studying diagrams in a textbook, static representations that often failed to convey the three-dimensionality and dynamism of the subject matter. But with 3D printing, the student can now print a physical model of the molecule, holding it in their hands, rotating it, and examining its structure from every angle. This ability to transform abstract concepts into tangible experiences is a game-changer for education, making complex ideas more accessible and comprehensible.
- 2. Increased Student Engagement: The impact of 3D printing on student engagement is equally profound. When students are no longer passive recipients of information but active participants in the learning process, their motivation and interest levels soar. 3D printing empowers students to become designers, creators, and experimenters, transforming the classroom into a dynamic space of exploration and discovery.
- 3. Examples: 3D Printed Robots, Anatomical Models: Consider the example of a student designing and printing their own robot. This project integrates multiple STEM disciplines, requiring the student to apply knowledge of mechanics, electronics, and programming. The process of designing, building, and testing a robot is inherently engaging, fostering a deeper understanding of engineering principles than any textbook could provide. Or imagine a biology class where students are studying the human body. 3D printing can be used to create accurate models of human organs, allowing students to explore their complex anatomy in a way that is both visually stunning and intellectually stimulating.
B. Design Thinking and Problem-Solving: Training the Next Generation of Innovators
Beyond its ability to enhance the learning of specific subject matter, 3D printing is also a powerful tool for developing essential skills that will serve students well in an increasingly complex and rapidly changing world. It is fostering design thinking, problem-solving abilities, and the capacity to translate ideas into tangible solutions.
- 1. Encouraging Creative Solutions: 3D printing encourages students to adopt a mindset of innovation, to look at challenges not as obstacles but as opportunities for creative problem-solving. It empowers them to ask “How can I make this better? How can I create something new?”
- 2. Developing Critical Thinking: The process of designing and printing an object demands that students engage in critical thinking at every stage. They must consider factors such as material properties, design constraints, structural integrity, and functional requirements. This process of careful planning, execution, and evaluation hones their critical thinking skills, preparing them to tackle complex problems in any field they may choose to pursue.
- 3. Examples: Assistive Devices, Environmental Solutions: 3D printing is already being used to empower students to design and print assistive devices for people with disabilities, creating customized solutions that improve quality of life. Furthermore, students are using 3D printing to create models of sustainable housing and to design solutions for environmental challenges, fostering a sense of social responsibility and empowering them to become agents of positive change.
C. Cross-Curricular Integration: 3D Printing Across the Curriculum
The true power of 3D printing in education lies in its versatility, its ability to transcend the boundaries of individual subjects and to become integrated across the entire curriculum. It is not simply a tool for science and math, but a technology that can enhance learning in virtually every discipline.
- 1. Science: Molecular Models, Geological Formations: In science classrooms, 3D printing can bring the microscopic world to life, allowing students to visualize the intricate structures of molecules and crystals. It can also make the vastness of geological time tangible, enabling them to hold 3D models of geological formations in their hands and to understand the forces that have shaped our planet.
- 2. Technology: CAD Software, Printer Operation: 3D printing also equips students with valuable technical skills that are increasingly in demand in today’s technology-driven world. They learn to use computer-aided design (CAD) software, the digital tools that underpin the creation of 3D models, and they gain hands-on experience in operating the printers themselves, understanding the principles of additive manufacturing.
- 3. Engineering: Structural Design, Mechanical Systems: Engineering classes are transformed by 3D printing, becoming dynamic laboratories where students can design and test structural components, build scale models of bridges and buildings, and create complex mechanical systems. This experiential learning provides them with a real-world understanding of engineering principles, bridging the gap between theory and practice.
- 4. Mathematics: Geometric Shapes, Scaling: Even the abstract realm of mathematics can be made more concrete and engaging with 3D printing. Students can explore the properties of geometric shapes, visualize the principles of scaling and proportion, and create tangible representations of complex mathematical concepts, making the often-daunting world of numbers and equations more accessible and less intimidating.
D. Accessibility in Education: Breaking Down Barriers
For too long, access to advanced manufacturing tools has been concentrated in the hands of elite universities and well-funded research institutions, perpetuating a divide between those who have the resources to create and innovate and those who do not. But 3D printing is helping to break down these barriers, democratizing access to the tools of creation.
- 1. Lowering Costs for Prototyping: By significantly lowering the cost of prototyping, 3D printing is making it possible for schools with limited budgets, and even individual students working on personal projects, to engage in the process of design and invention.
- 2. Increasing Access to Manufacturing Tools: This increased affordability is translating into greater access to manufacturing tools for a wider range of students, regardless of their socioeconomic background or the resources of their schools. 3D printing is fostering a more level playing field, empowering a new generation of innovators and ensuring that talent and creativity are not limited by privilege.
3D Printing for Everyday Problem-Solving: Making Life Easier, One Print at a Time
While the transformative power of 3D printing is evident in the realms of DIY projects and education, its impact is also being felt in the more mundane, yet no less significant, sphere of everyday life. This technology is proving to be a remarkably versatile tool for solving a wide array of common problems, making our lives easier, more efficient, and more tailored to our individual needs.
A. Custom Tools and Jigs: The Right Tool for the Job
The adage “the right tool for the job” speaks to the importance of having implements that are precisely suited to the task at hand. Yet, in a world of mass-produced tools, we often find ourselves compromising, making do with tools that are “close enough” but not ideal. 3D printing is changing this paradigm, empowering individuals to create tools that are perfectly tailored to their specific needs.
- 1. Specialized Tools for Home and Workshop: Imagine encountering a task around the house or in the workshop that requires a tool with a highly specialized design. In the past, finding such a tool might have involved a frustrating and time-consuming search, or even the acceptance that the task simply could not be done efficiently. With 3D printing, however, the solution is at hand. Individuals can design and print tools that are precisely tailored to the task, no matter how specialized or unusual it may be.
- 2. Improving Efficiency and Accuracy: The ability to create custom tools translates directly into increased efficiency and accuracy. When a tool is designed to fit a specific task perfectly, it minimizes wasted motion, reduces the risk of errors, and allows the user to perform the task with greater precision and control.
- 3. Examples: Cable Organizers, Phone Stands: Consider the humble cable organizer, a simple device that can transform a tangled mess of wires into a neat and orderly arrangement. With 3D printing, individuals can design cable organizers that are precisely tailored to their specific needs, accommodating the number and type of cables on their desk or entertainment center. Or imagine a phone stand that holds a device at the perfect viewing angle, customized to fit a particular model of phone or tablet. These are just two examples of how 3D printing can be used to create simple yet highly effective tools that enhance our daily lives.
B. Household Repairs: Don’t Throw It Away, Fix It!
As discussed earlier, 3D printing is playing a crucial role in challenging our culture of disposability, empowering us to repair broken items rather than simply replacing them. This shift towards a more repair-oriented mindset has significant environmental and economic benefits.
- 1. Printing Replacement Parts: Instead of discarding a broken appliance or a piece of furniture because of a single damaged component, individuals can now print a replacement part and restore the item to full functionality. This simple act of repair not only saves money but also reduces the amount of waste that ends up in landfills.
- 2. Modifying Existing Objects: But 3D printing is not just about fixing what is broken; it is also about enhancing what already exists. Individuals can use this technology to modify existing objects, adapting them to new purposes or improving their functionality.
- 3. Examples: Handles, Supports, Adapters: A new, more comfortable handle for a kitchen gadget, a support to prevent a shelf from wobbling, an adapter that allows two different devices to be connected – these are just a few examples of how 3D printing can be used to extend the life of household items and to make them more versatile and user-friendly.
C. Assistive Devices: Improving Lives with 3D Printing
Perhaps one of the most profound and socially significant applications of 3D printing lies in its ability to create customized assistive devices for individuals with disabilities. This technology is not only improving functionality but also enhancing the quality of life and promoting greater inclusion.
- 1. Personalized Aids for Disabilities: 3D printing allows for the creation of assistive devices that are precisely tailored to the unique needs of each individual, taking into account their specific physical challenges and limitations.
- 2. Low-Cost Accessibility Solutions: Compared to traditional methods of manufacturing assistive devices, which often involve expensive and time-consuming processes, 3D printing offers a far more affordable and efficient alternative. This cost-effectiveness is making these essential solutions more accessible to a wider population, ensuring that individuals with disabilities have access to the tools they need to live full and independent lives.
- Examples: Adapted Utensils, Grips: Consider the design and fabrication of adapted utensils for individuals with limited hand mobility. 3D printing allows for the creation of customized grips that conform perfectly to the user’s hand, making eating a more comfortable and dignified experience. Similarly, 3D-printed grips can be designed for a variety of tools, from gardening implements to writing instruments, empowering individuals with disabilities to participate more fully in everyday activities.
D. Rapid Prototyping: From Idea to Reality, Fast!
As we have seen in the context of DIY projects, 3D printing is a powerful tool for rapid prototyping, allowing creators to quickly translate their ideas into tangible form. This capability is not only valuable for hobbyists but also for entrepreneurs, inventors, and anyone with a vision they wish to bring to life.
- 1. Quickly Creating Prototypes: 3D printing enables the swift creation of physical prototypes, providing a tangible representation of an abstract idea. This rapid turnaround is invaluable for testing designs, gathering feedback, and iteratively refining a concept.
- 2. Testing Designs: Whether it’s an aspiring entrepreneur developing a new product or an individual with a novel idea for a gadget, 3D printing empowers them to bypass the lengthy and expensive processes of traditional manufacturing and to bring their vision to fruition with unprecedented speed and efficiency.
Challenges and Considerations: A Realistic Look
While the transformative potential of 3D printing is undeniable, it is important to acknowledge that, like any technology, it also presents certain challenges and limitations. A balanced perspective requires that we consider not only the exciting possibilities but also the practical considerations that accompany the adoption and use of this technology.
- A. Learning Curve: While 3D printers are becoming increasingly user-friendly, the process of designing and printing a 3D object still involves a learning curve. Users must acquire proficiency in CAD software to create digital models, and they must also develop an understanding of the printing process itself, including factors such as material properties, printer settings, and troubleshooting techniques.
- B. Material Costs: The cost of materials used in 3D printing, primarily in the form of filaments, can vary significantly depending on the type of material. While some common materials, such as PLA, are relatively inexpensive, more specialized materials, such as those with enhanced strength or flexibility, can be considerably more costly.
- C. Maintenance: 3D printers, like any mechanical device, require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. This maintenance may include cleaning, calibration, and the occasional replacement of parts.
- D. Design Limitations: While 3D printing excels at creating objects with complex geometries, there are still certain design limitations that users must be aware of. Overhangs, intricate details, and the need for support structures can all pose challenges, requiring designers to adapt their models accordingly.

The Future is in Your Hands
In spite of these challenges, the long-term potential of 3D printing remains virtually limitless. This technology is not merely a passing fad; it is a fundamental shift in the way we create and interact with the physical world. It is empowering individuals, transforming industries, and driving innovation across a wide spectrum of fields.
To reiterate, 3D printing is placing the power of manufacturing directly into the hands of hobbyists, enabling them to design and create custom tools, personalized items, and replacement parts with unprecedented ease. It is revolutionizing STEM education, making learning more hands-on, engaging, and accessible to students of all backgrounds. And it is providing everyday people with new and innovative ways to solve problems, enhance their lives, and express their creativity.
As 3D printing technology continues to evolve, becoming more affordable, more user-friendly, and more capable, it is poised to unleash a wave of innovation that will transform our world in ways we can only begin to imagine. The future of creation is no longer confined to the realm of large-scale factories and specialized industries; it is increasingly in the hands of individuals, armed with the power to bring their ideas to life, one layer at a time. The tools are now available; the only limit is the boundless capacity of human imagination. So, let us embrace this technology, unleash our inner inventors, and embark on the exciting journey of printing our world anew.