Understanding how a 3D printer works can help you make better models. The technology behind 3D printers is becoming more and more commonplace, with new applications being discovered all the time. However, many people are still in the dark about how these machines work.
In this blog post, we’ll explore why understanding the basics of how a 3D printer works can help you create better objects. By learning about things like layer thickness and nozzle size, you can be sure that your prints will come out looking just the way you want them to!
How 3D printers work
If you’re new to 3D printing, the process can seem a bit daunting. But understanding how your printer works can help you maximize your creations. FDM 3D printers work by heating a polymer filament until it melts and extrudes out of a nozzle, creating a solid object.
The machine then moves the print head to make copies of the object layer by layer. When finished, that’s your 3D print! By understanding this process, you can troubleshoot issues with your printer and produce high-quality prints.

The benefits of understanding the basics of how a 3D printer works
If you’re looking to get the most out of your 3D printer, it’s important to have a basic understanding of how the machine works.
By knowing how the printer extrudes melted polymer filament and builds objects layer by layer, you can make more informed decisions about your designs and prints.
This knowledge can help you troubleshoot issues that may arise during printing, as well as optimize your designs for better results.
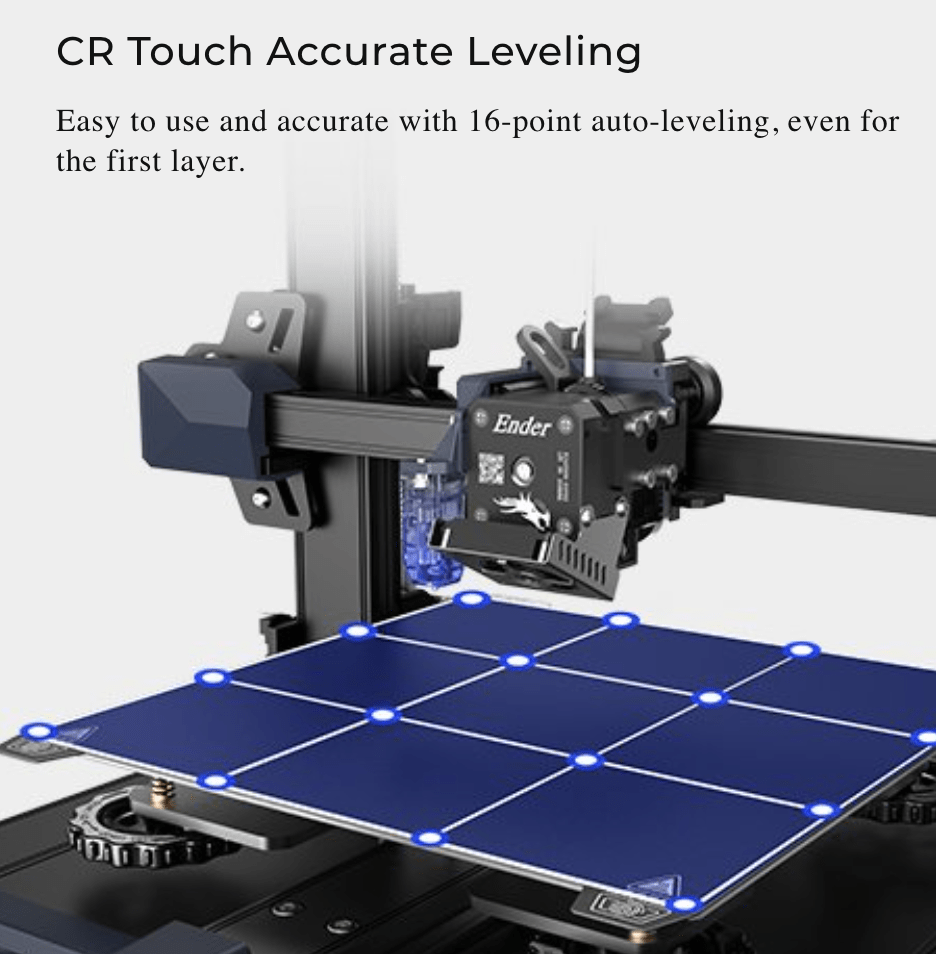
Z-Axis
The Z-axis is the axis (or “direction”) that is perpendicular to the print bed and parallel to the extruder nozzle.
When a 3D printer is in motion, the extrusion nozzle will travel in this axis from the bottom of the build bed all the way to the top. As the nozzle travels up, it creates a new layer of the molten polymer at each point it crosses.

Layer thickness
The layer thickness of a 3D print can have a big impact on the final product. A thicker layer will make for a stronger, more durable print.
In comparison, a thinner layer will result in a lighter and more detailed object. To get the most out of your 3D printer, it’s important to understand how changing the layer thickness can affect your objects.

Layer Thickness for 3D Printing by Material
As a rule of thumb, layer thickness should be thinner with more flexible materials like PLA and thicker with more brittle ones like ABS.
You may be able to achieve a better surface finish and quality with a thinner layer as well. However, this is by no means a hard-and-fast rule, and you will have to experiment to find your own ideal setting.
Nozzle size
Nozzle size plays a big role in how your 3D prints turn out. A larger nozzle will result in a thicker extrusion, while a smaller nozzle will create thinner, more delicate features.
If you’re unsure what size to use, start with the largest nozzle your printer can accommodate and work your way down until you find the sweet spot for your project.
When using a dual extrusion printer, the nozzle sizes, volume, and fan speeds will vary between the material you are printing. To ensure the best print quality, we recommend starting with the same nozzle size for both materials.
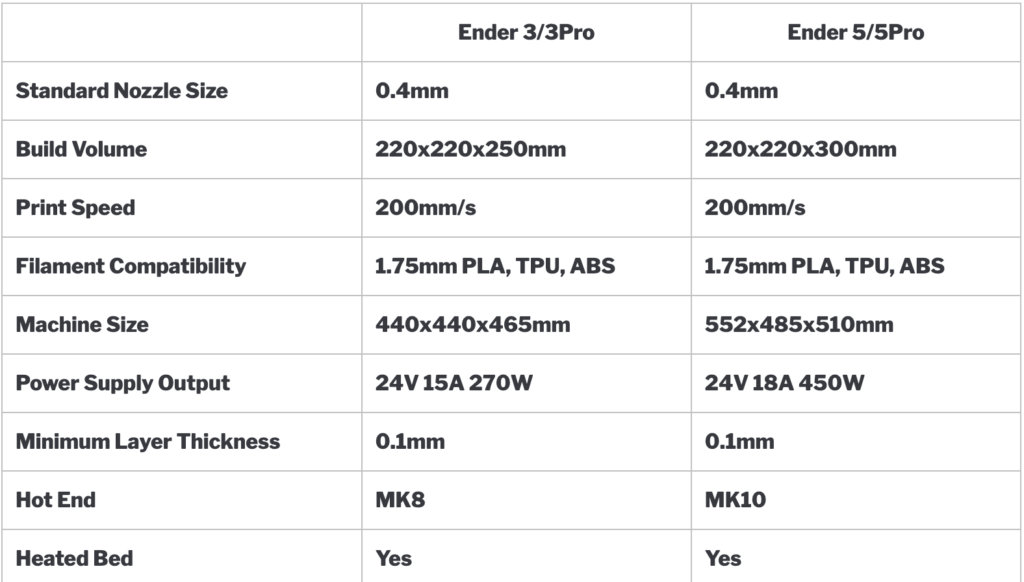
Filament
Filament Diameter is the diameter of the filament spool in your printer. This measurement will vary depending on the manufacturer of your printer and can be found by checking your printer’s manual.
Want more? Click Here!
Thanks,
Bullwinkle
