 The following are some of the most important reasons why ABS is the most commonly used material in 3D Printing: ABS is a tough and durable material. ABS allows for a fast printing speed. ABS offers a high strength-to-weight ratio. ABS material has been proven to be reliable. ABS requires no priming or painting. ABS is available in different colors. ABS can be used to make useful and functional parts.
The following are some of the most important reasons why ABS is the most commonly used material in 3D Printing: ABS is a tough and durable material. ABS allows for a fast printing speed. ABS offers a high strength-to-weight ratio. ABS material has been proven to be reliable. ABS requires no priming or painting. ABS is available in different colors. ABS can be used to make useful and functional parts.
Why ABS?
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is one of the most commonly used materials in 3D Printing for several reasons:
1. Durability: ABS is known for its robustness and resistance to wear and tear, making it ideal for functional parts and prototypes.
2. High-Temperature Resistance: ABS can withstand higher temperatures compared to other common 3D printing materials like PLA (Polylactic Acid).
3. Ease of Use: ABS is relatively easy to work with, requiring no specialized equipment beyond a heated print bed, which is standard on most 3D printers.
4. Finish Quality: ABS can be easily sanded and painted, making the final product a better finish.
5. Cost-Effectiveness: ABS is generally affordable, making it a popular choice for both hobbyists and professionals alike.
Who is this Blog for?
1. Beginners: If you’re new to 3D Printing and want to learn the basics, this book will guide you through the fundamentals, including how to choose materials like ABS.
2. Hobbyists: For those who have some experience but want to delve deeper, this book offers advanced tips and techniques for mastering 3D Printing with ABS.
3. Professionals: Engineers, designers, and other professionals who use 3D Printing in their work will find valuable insights into optimizing print quality, durability, and functionality using ABS.
4. Educators: Teachers and instructors looking to incorporate 3D Printing into their curriculum will find this book a useful resource for understanding the material science behind ABS and its applications in 3D Printing.
5. Entrepreneurs: If you’re looking to start a 3D printing business, this blog will provide you with the know-how to choose the right materials and equipment, with a focus on the advantages of ABS.
By the end of this blog, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of 3D Printing with ABS, equipped with the knowledge to create high-quality, durable, and functional 3D-printed objects.
Choosing a 3D Printer
Selecting the right 3D printer is the first crucial step in your 3D printing journey. Here are some factors to consider:
1. Type of Printer: Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) or Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) printers are commonly used for ABS printing due to their capability to print at high temperatures.
2. Build Volume: Choose a printer with a build volume that matches the size of the objects you plan to print.
3. Heated Bed: ABS tends to warp during the cooling process, so a heated bed is essential for better adhesion and print quality.
4. Temperature Range: Ensure the printer can reach the temperatures required for ABS, typically between 210–250°C for the extruder and 80–110°C for the bed.
5. Resolution: The layer height and printing speed will determine the resolution of your print. Lower layer heights generally yield better resolution but take longer to print.
6. Reliability and Support: Look for printers from reputable manufacturers that offer good customer support and have a large user community.
7. Budget: ABS-compatible printers come in a wide range of prices, so find one that fits your budget but doesn’t compromise on essential features.
Understanding ABS Material
Before you start printing, it’s essential to understand the properties and characteristics of ABS:
1. Temperature Resistance: ABS has a higher melting point, making it suitable for objects that will be exposed to heat.
2. Durability: ABS is strong, impact-resistant, and somewhat flexible, making it ideal for functional parts.
3. Post-Processing: ABS can be sanded, painted, and glued, offering flexibility in post-processing.
4. Health and Safety: ABS can produce fumes during Printing, so it’s advisable to print in a well-ventilated area or use printers with built-in air filters.
5. Storage: ABS is hygroscopic, meaning it absorbs moisture from the air. Store it in a dry place to maintain its print quality.
Tools and Supplies Needed
Here’s a list of additional tools and supplies you may need:
1. Build Surface: Kapton tape, painter’s tape, or a glue stick can help improve bed adhesion.
2. Calipers: For precise measurements and adjustments.
3. Spatula or Scraper: To remove the finished print from the build plate.
4. Sanding Paper: For post-processing to smooth out rough edges.
5. Paints and Primers: If you plan to paint your ABS prints.
6. Ventilation: A fan or exhaust system if you’re printing in a confined space.
7. Pliers and Tweezers: For removing support structures and handling hot components.
8. Cleaning Supplies: Isopropyl alcohol or similar for cleaning the build plate.
9. Safety Gear: Gloves and a mask for handling hot or sharp objects and fumes.
By understanding these basics, you’ll be well-prepared to start your 3D printing journey with ABS. The next section will dive deeper into each aspect, offering expert tips and tricks to help you master 3D Printing with ABS.
Setting Up Your 3D Printer
Getting your 3D printer up and running is an exciting step, but it’s important to proceed carefully to ensure the best results. Here’s how to go about it:

Unboxing and Assembly
1. Unboxing: Carefully remove all parts from the box. This usually includes the printer frame, build plate, extruder, power supply, and other accessories.
2. Inventory Check: Verify that all parts are included per the instruction manual. Missing or damaged parts should be reported to the manufacturer immediately.
3. Assembly: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for assembly. This often involves attaching the build plate, installing the extruder, and connecting various cables.
4. Power Up: Once assembled, plug in the printer and power it up to ensure everything is working as expected.
5. Firmware: Update to the latest firmware as recommended by the manufacturer.
6. Software: Install any software that comes with your printer, or download recommended slicing software compatible with your printer model.
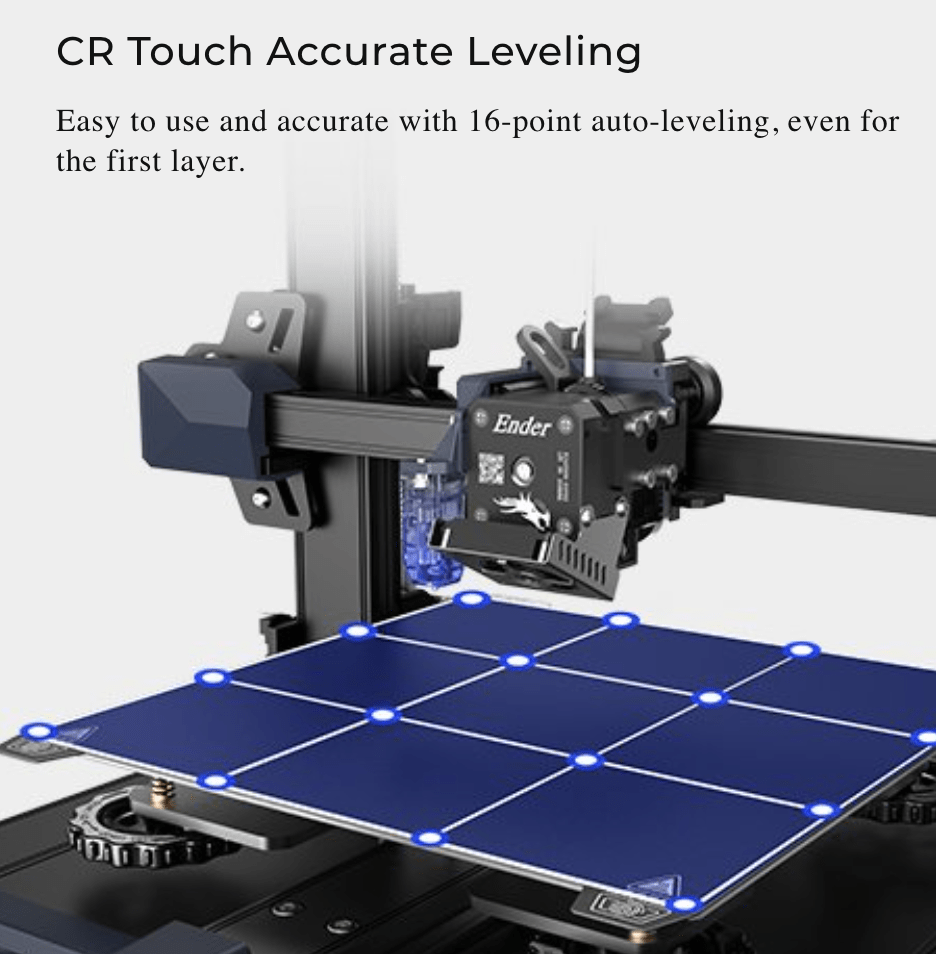
Calibration
1. Leveling the Bed: Most printers require you to manually or automatically level the build plate to ensure it’s parallel to the movement of the extruder.
2. Z-Axis Calibration: Adjust the distance between the extruder nozzle and the build plate to ensure optimal adhesion and print quality.
3. Extruder Calibration: This ensures that the extruder feeds the correct amount of filament during Printing.
4. Temperature Settings: Perform test prints to find the optimal temperature settings for both the extruder and the heated bed when using ABS.
5. First Print: After calibration, it’s advisable to start with a simple test print to verify that everything is set up correctly.
Safety Precautions
1. Ventilation: ABS fumes can be toxic, so ensure proper ventilation in your printing area.
2. Electrical Safety: Make sure your printer is properly grounded and keep liquids away from all electrical components.
3. Hot Surfaces: The extruder and heated bed get very hot during Printing. Avoid touching these areas to prevent burns.
4. Moving Parts: Keep fingers, hair, and clothing away from all moving parts during operation.
5. Emergency Shutdown: Know how to quickly shut down your printer in case of an emergency, such as a jam or other malfunction.
6. Child and Pet Safety: Keep children and pets away from the printer both during operation and when it’s idle to avoid accidents.
7. Fire Safety: Keep a fire extinguisher nearby, especially if you plan to leave the printer unattended for long periods.
It is crucial to ensure your 3D printer is properly set up and calibrated. This will give you a better chance of achieving success in your 3D printing endeavors.
The previous information provided detailed information on designing and printing with ABS, which is a versatile material with a lot of potential. By following these guidelines, you will be able to unlock the full potential of ABS and create amazing 3D prints.
3D Printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a revolutionary technology that enables the creation of three-dimensional objects from a digital design. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods that require cutting away material to create a shape, 3D Printing builds up material layer by layer to form the object. This technology has transformed several industries, including automotive, healthcare, aerospace, and consumer goods. It has made rapid prototyping possible, reduced waste, and allowed for highly customized designs.
Thank you,
Bullwinkle


