3D Printing, also known as additive manufacturing, creates a three-dimensional object from a digital model. It works by adding material layer by layer until the object is complete. 3D Printing has a wide range of applications across various industries, including:
- Aerospace and defense: 3D Printing is used to produce lightweight, high-strength parts for aircraft and spacecraft. For example, GE Aviation uses 3D Printing to make fuel nozzles for its LEAP jet engines.
- Automotive: 3D Printing produces prototypes, tooling, and even end-use parts for cars and trucks. For example, BMW uses 3D Printing to build prototypes of new car models.
- Medical: 3D Printing is used to produce custom prosthetics, implants, and surgical instruments. For example, Stratasys uses 3D Printing to create custom cranial implants for patients with skull defects.
- Construction: 3D Printing is used to produce prefabricated construction components, such as wall panels and roof trusses. For example, ICON uses 3D Printing to build affordable homes in developing countries.
- Consumer goods: 3D Printing is used to produce a variety of consumer goods, such as toys, jewelry, and home décor items. For example, Formlabs uses 3D Printing to make custom jewelry for its customers.
In addition to these specific industries, 3D Printing is also used in a variety of other applications, such as:
- Education: 3D Printing is used in schools and universities to teach students about engineering, design, and manufacturing.
- Research: 3D Printing is used in research laboratories to develop new materials and products.
- Art and design: 3D Printing is used by artists and designers to create unique and innovative works.
3D Printing is a rapidly developing technology with the potential to revolutionize many industries. As the technology continues to mature and become more affordable, we can expect to see even more innovative and groundbreaking applications of 3D Printing in the years to come.
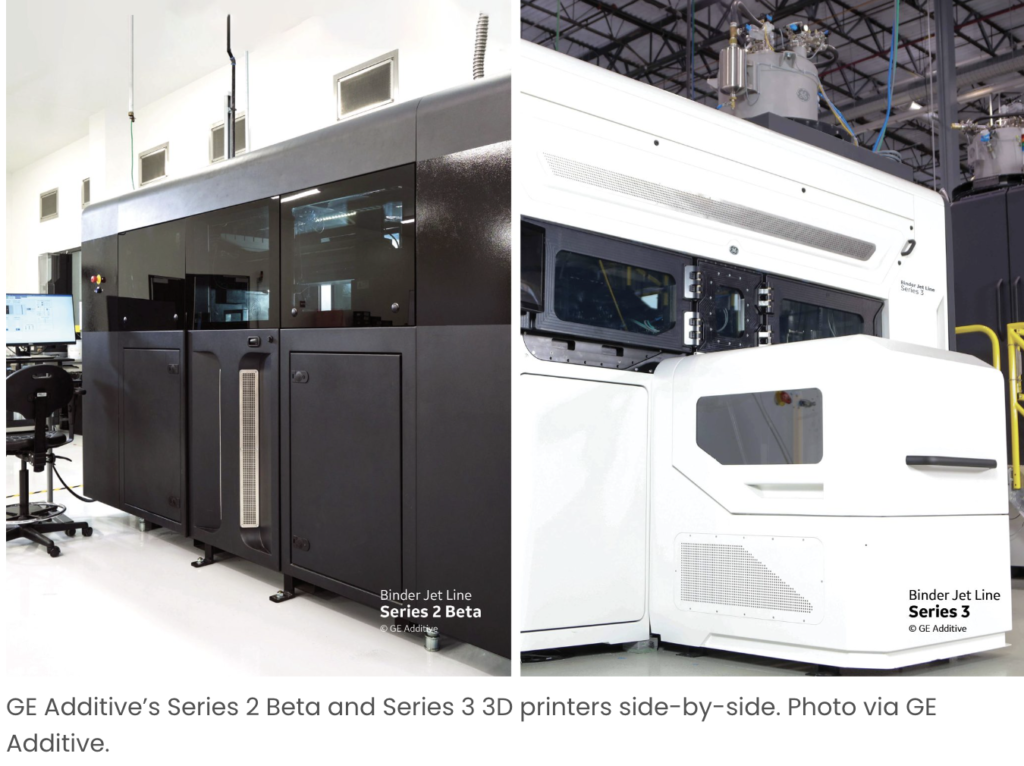

What are the Applications of 3D Printing?
3D Printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has a plethora of applications across various industries. In the medical field, it is used for creating custom prosthetics, dental implants, and even bio-printing tissues and organs. The aerospace and automotive sectors employ 3D Printing to fabricate lightweight components and intricate designs, optimizing performance and reducing waste.
In construction, 3D Printing is revolutionizing the creation of buildings and structures, allowing for innovative designs and sustainable materials.
The fashion industry also utilizes 3D Printing to produce unique and customizable garments and accessories.
Additionally, 3D Printing is widely used for creating prototypes, enabling rapid product development and testing in fields like consumer electronics and industrial design.
How to Design Models for 3D Printing?
Designing models for 3D Printing involves several steps. Initially, a concept is developed and then translated into a 3D model using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software.
During this phase, designers must consider the limitations and capabilities of the chosen 3D printing technology and material. The model is then converted into a format readable by 3D printers, typically STL or OBJ.
Before Printing, the model is sliced into layers using slicing software, which also allows for the adjustment of print settings such as resolution, infill, and support structures. Proper orientation and support are crucial to avoid deformation and ensure accuracy and strength in the final print.
Finally, designers should conduct a thorough review of the model to identify and rectify any errors or potential issues before printing.
What Materials Can be Used for 3D Printing?
3D Printing can accommodate a diverse range of materials. Plastics, such as PLA and ABS, are the most common due to their versatility and ease of use. Resins are used in stereolithography (SLA) printing for high-detail models.
Metals, including titanium and stainless steel, are employed for creating durable and robust components, especially in aerospace and medical applications.
Ceramics are utilized for creating objects that require high heat resistance and hardness. Additionally, composite materials, which combine the properties of different materials, are used to meet specific requirements, such as lightweight strength. Emerging materials like conductive filaments and bio-based materials are expanding the possibilities of 3D printing applications.
How Long Does it Take to 3D Print an Object?
The duration of a 3D print job depends on several factors, including the size and complexity of the object, the printing technology used, layer height, and print speed. Smaller objects with simple geometries may only take a few hours, while larger, more complex models can require days. For instance, FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) printers, which are common in hobbyist settings, may take longer to print compared to industrial-grade SLA (Stereolithography) or SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) printers due to differences in speed and precision. Additionally, higher-resolution prints with finer layers will take longer than lower-resolution prints with thicker layers.

What are Common 3D Printing Problems and Solutions?
3D Printing can encounter several issues, each with its own set of solutions. Warping occurs when the print cools unevenly, causing the edges to lift. A heated print bed and enclosure can mitigate this.
Another common issue is stringing, where thin strands of material form between parts of the print. Proper retraction settings and optimal printing temperature can resolve stringing.
Clogging, often caused by impurities in the filament or a mismatch in temperature, can be addressed by cleaning or replacing the nozzle and using quality filament. Layer shifting can be corrected by ensuring the printer’s belts are tight, and the frame is stable.
Regular maintenance, calibration, and fine-tuning of the printer settings are crucial in preventing and solving most 3D printing problems.
Is 3D Printing Cost-Effective?
The cost-effectiveness of 3D Printing depends on the use case. For prototyping and small-batch production, 3D Printing is often more cost-effective compared to traditional manufacturing methods, as it reduces lead times and eliminates the need for molds and tooling. However, for large-scale production, conventional methods like injection molding may still be more economical due to their speed and efficiency.
The price of materials, energy consumption, and maintenance also influences the cost of 3D Printing. Advances in 3D printing technology and the increasing availability of affordable printers and materials continually enhance the cost-effectiveness of 3D Printing across various applications.
Bullwinkle


